triSure Procare More than NIPT
- 25 7,018 mutations linked to the 25 most prevalent single-gene disorders. These conditions may impact quality of life and require early intervention to prevent them from going unnoticed as the child develops.
- 18 7,535 mutations related to 18 recessive diseases from mothers.
- 27 27 numerical chromosome abnormalities for fetus and microdeletion.
Three main causes of genetic abnormalities in the fetus
Numerical chromosome
abnormalities
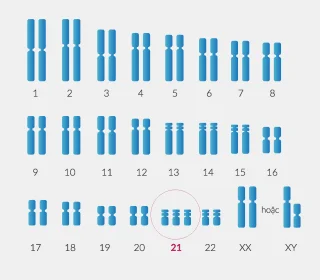
Conventional NIPT test
Abnormalities caused by mutations
in recessive genes
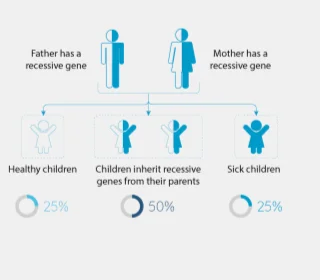
Carrier - recessive diseases screening
Abnormalities caused by de novo mutations
in dominant genes
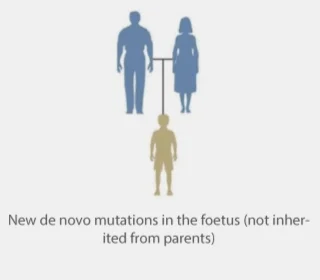
Single-gene NIPT

Why should we care for single-gene disorders?
25 prevalent single-gene disorders have a cumulative frequency higher than Down syndrome. More important, these are serious diseases that affect the quality of children's lives, but cannot be detected by conventional NIPT testing. Early screening within nine weeks' gestation will help timely intervention and effective newborn treatment.
The challenge of monodominant disease is mainly caused by mutations that are not hereditary
- 60 percent of severe single-gene diseases after birth are caused by de novo mutations in the foetus (inherited from neither parent)(1).
- De novo mutations in the foetus increase with paternal age (not related to maternal age), i.e. the older the father (>40 years old), the greater the risk of having a child with a dominant genetic disease caused by a de novo mutation(2).
(1) Baird, P. A. et al. Am. J. Hum.Genet. 42, 677-693 (1988)
(2) ACMG, Practice guideline, June 2008
Number of the novo mutations called
De novo variants
by paternal age
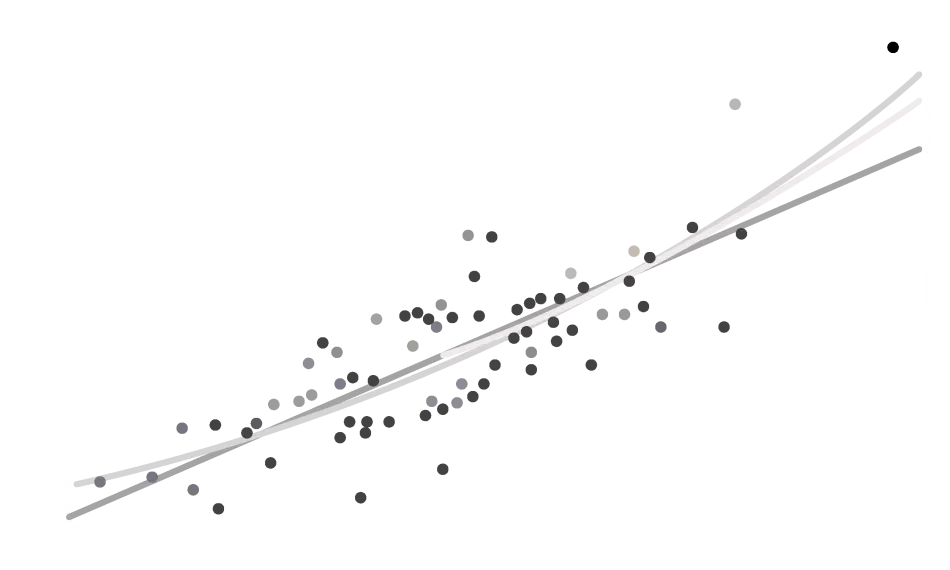
Age of father at conception of child
De novo mutations in the foetus increase with paternal age
Benefits of NIPT test for single gene disorders
Incidence at birth
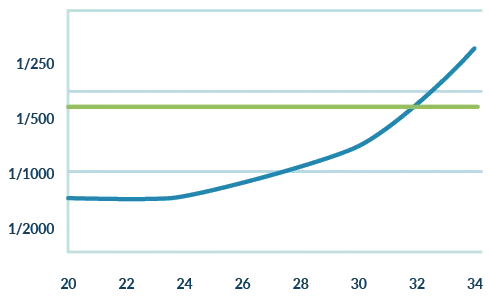
Down syndromel(*)
25 dominant single-gene diseases(**)
Maternal age
A cumulative frequency 25 dominant single-gene diseases higher than Down syndrome
(*) Snijders et al. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Mar; 13(3):167-70.
(**) GeneReviews. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/
25 prevalent single-gene disorders
Skeletal Disorders
Achondroplasia, Hypochondroplasia, CATSHL syndrome, Thanatophoric dysplasia, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Osteogenesis imperfecta.
Craniosynostosis syndromes
Antley-Bixler syndrome, Apert syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Jackson_Weiss syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Muenke syndrome.
Noonan Spectrum Disorders
Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, Costello syndrome, LEOPARD syndrome, Noonan syndrome.
Syndromic Disorders
Alagille syndrome, CHARGE syndrome, Cornelia de Lange syndrome, Epileptic encephalopathy, Intellectual disability, Rett syndrome, Sotos syndrome, Tuberous sclerosis.
Who should take the single-gene NIPT test?

Advanced paternal age

Abnormal ultrasound findings

Family history of hereditary conditions

Want to know
